This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
- Home
- About Us
- Examinations

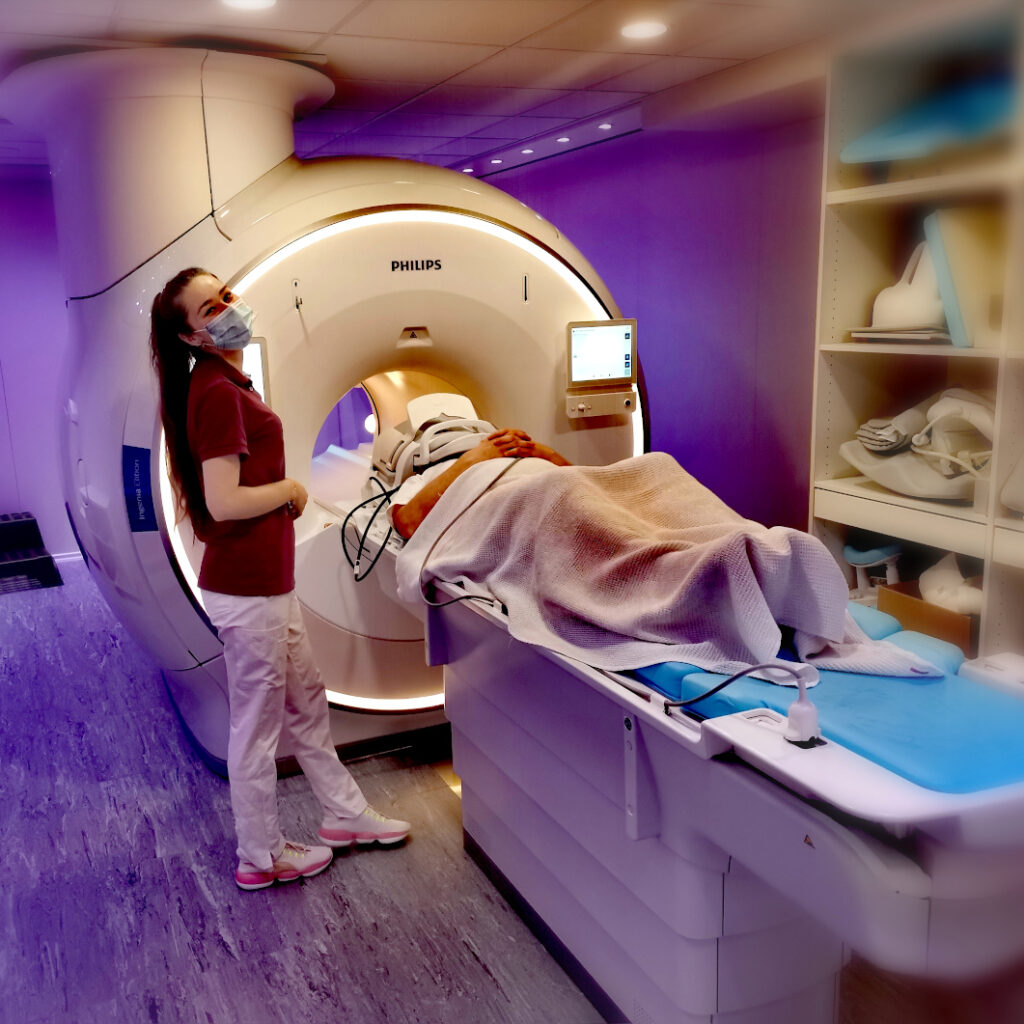
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
MRI
A small river named Duden flows by their place and supplies it with the necessary regelialia. It is a paradisematic country, in which roasted parts of sentences fly into your mouth. Even the all-powerful Pointing has no control about the blind texts it is an almost orthographic life One day however a small line of blind text by the name of Lorem Ipsum decided to leave for the far World of Grammar. The Big Oxmox advised her not to do so, because- Phone:+1 (859) 254-6589
- Email:info@example.com
3-Tesla High-field Magnetic Resonance Imaging

Mammary-MRI
Breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging

Prostate-MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Of The Prostate

CT
Computer Tomography

MG
Digital Mammography

SONO
Sonography (Ultrasound)

Mamma-Sono
14 MHz
Breast Ultrasound

Röntgen
Digital X-Ray
- Physicans
Your doctors at the Alte Slaine Radiological Centre

Dr. med.
Robert Küttner
Specialist in Radiology and Nuclear Medicine

Dr. med. univ.
Stephan Ortner
Specialist in Radiology

Dr. med. univ.
Eduard Kurkowski
Specialist in Radiology (employed physician)
- Vacancies
- Contact Us

Magnetic resonance tomography (MRI)
learn more

Mamma-MRI
learn more
An MRI examination of the breast, the so-called breast MRI, is a very sensitive method with which even small breast carcinomas and tumour precursors (DCIS) can be diagnosed.
This method can be used to detect tumours that are not yet visible in X-ray mammography and ultrasound. The detection rate of breast MRI is about 90 %.
The costs of breast MRI are usually covered by private health insurance companies without any problems.
Up to now, the statutory health insurance companies in Germany have only paid for breast MRI in exceptional cases; unfortunately, we cannot offer you any settlement via your statutory health insurance company.
If you would like to have the examination performed as a “self-payer”, this is of course also possible. Please do not hesitate to contact us, we will be happy to advise you.

Prostate MRI (mpMRI)
learn more
The multiparametric MRI examination of the prostate makes it possible to detect prostate cancer at an early stage or to exclude the presence of prostate cancer with a high degree of certainty. It is currently considered the most sensitive procedure for detecting changes that are suspicious for prostate cancer.
Private health insurances usually cover the costs of an mpMRI without any problems.
Unfortunately, the statutory health insurance funds in Germany do not currently pay for mpMRI, despite the recommendations in the prostate cancer guideline, i.e. it is not a standard benefit. However, patients with statutory health insurance can have the examination carried out by us as “self-payers”. We will be happy to advise you on this.

Computertomography
learn more

Digital Mammography
learn more
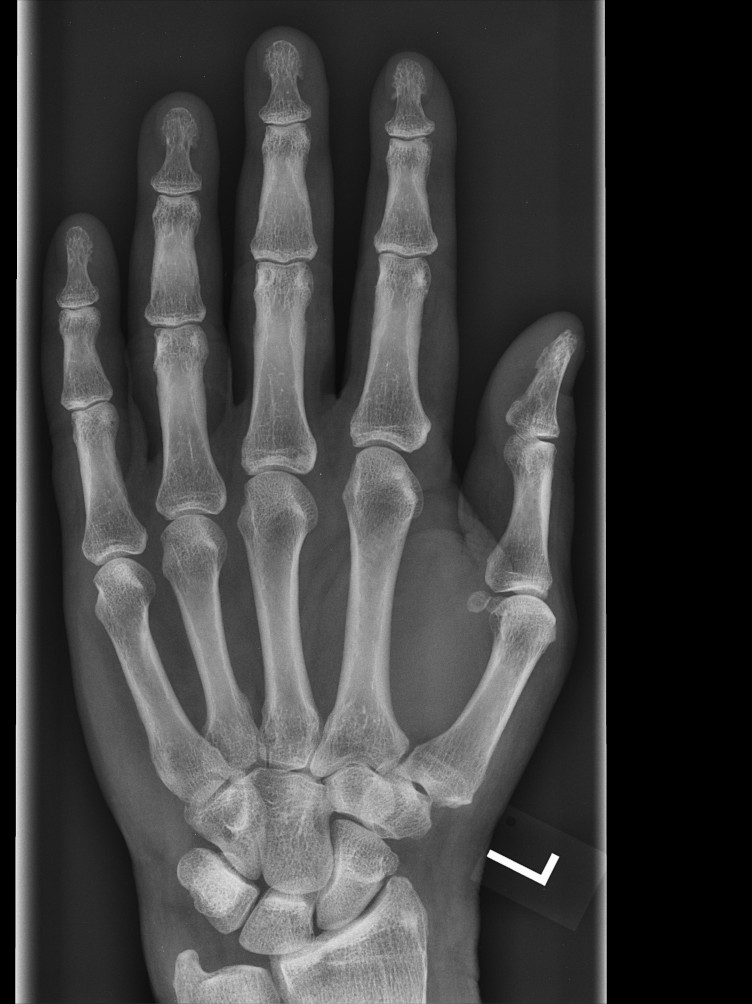
Digital X-Ray
learn more
This is an imaging procedure that uses X-rays to show mainly bone structures and also the lungs. This so-called conventional X-ray is increasingly being replaced by cross-sectional imaging (CT and MRI).
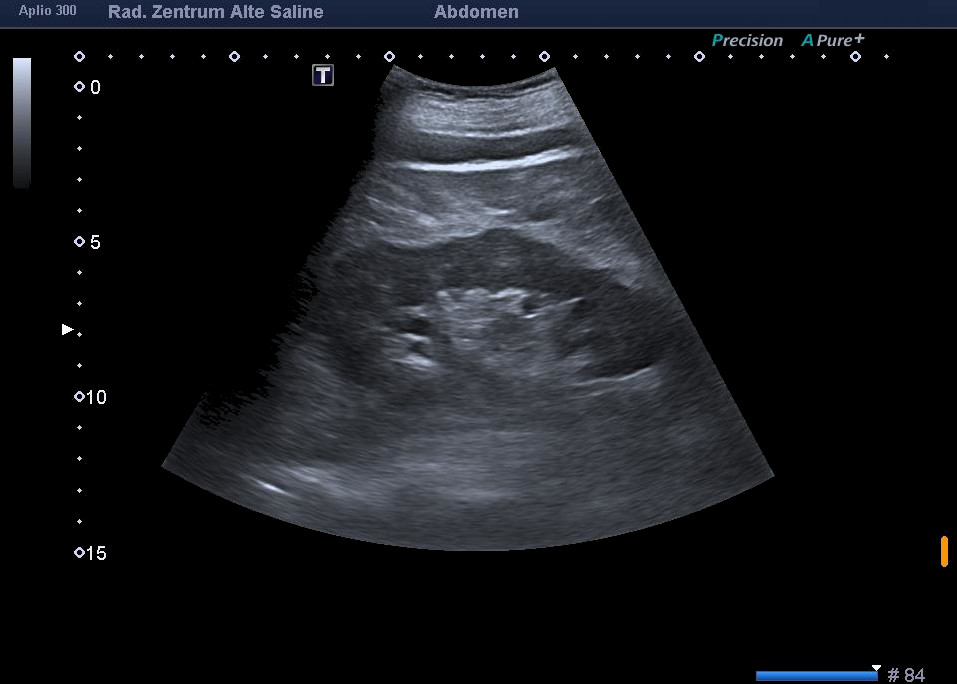
Ultrasound
learn more
In ultrasound, sound waves are emitted into the body from a transmitter guided by the doctor’s hand, reflected differently inside the body and sent back to the transmitter, which also acts as a receiver. A computer “translates” the reflected sound waves into an image on which the structures inside the body can be recognised. In addition to imaging the mammary gland, the ultrasound examination is often used in our practice to examine the abdominal organs and the thyroid gland.
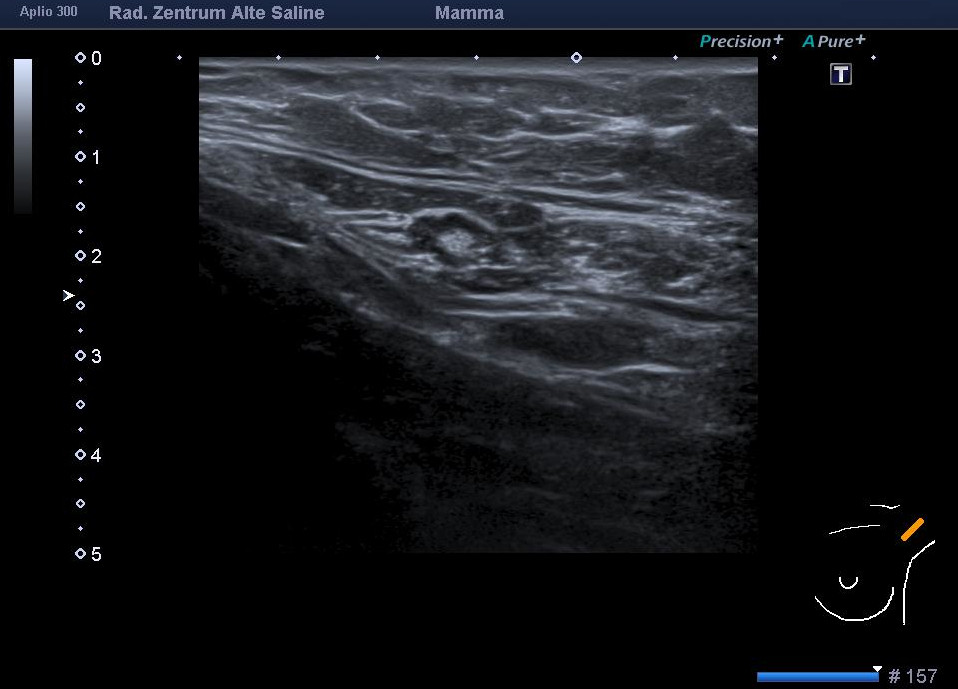
Mammary ultrasound
learn more
Sonography (=ultrasound) is now a firmly established and effective procedure for clarifying benign and malignant changes in breast tissue. In combination with a high-frequency transducer and colour-coded duplex sonography, even very small tumours can be detected with a relatively high degree of certainty, even in dense parts of the glandular tissue. Mammary sonography has been an integral part of the diagnostic spectrum in our practice for many years.